Webhooks Overview
Webhooks are a way for your app to receive live notifications of activity on your user’s accounts.
Currently we support 5 different event types:
- Message Received
- New Follower
- New Subscriber
- Purchase Received
- Tip Received
Here’s how to use them:
- Setup an endpoint on your backend to receive webhooks, this should be able to receive POST requests from our API
- Navigate to the Fanvue Developer Area, select your app and go to the Webhooks tab
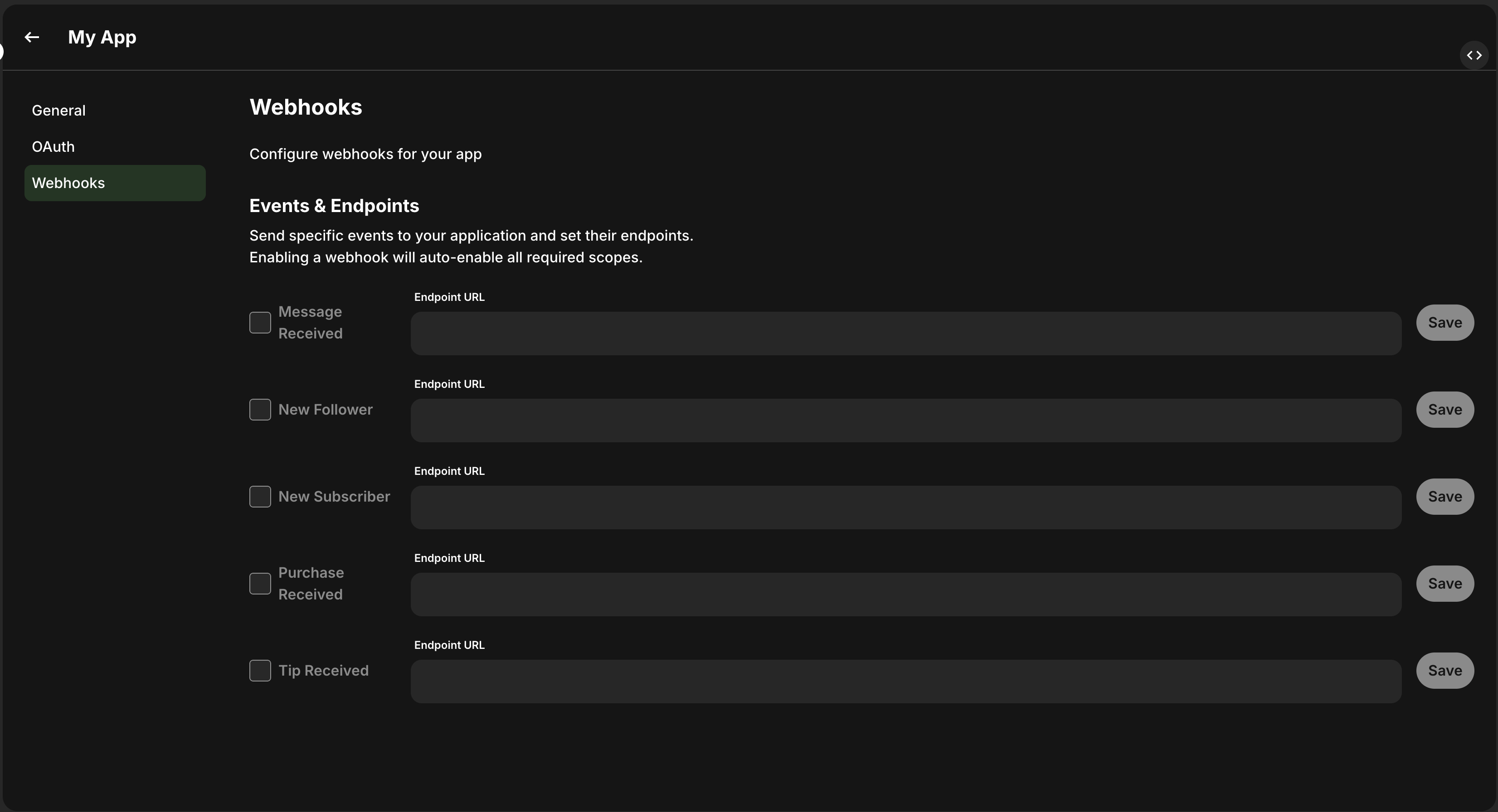
- Enter the desired URL

- Press Save and then enable the webhook by checking the box next to it
How deliveries work
- Each webhook is delivered as an HTTP POST with
Content-Type: application/json. - The request body contains an event-specific JSON payload.
- Your endpoint should return a 2xx response as soon as you successfully receive and persist the event.
Verifying webhook signatures
Every webhook request includes an X-Fanvue-Signature header. You should verify this signature on every request to ensure it came from Fanvue and was not tampered with.
Signature format
The header value has the format:
tis a Unix timestamp (seconds since epoch) indicating when the request was signed.v0is the HMAC-SHA256 signature encoded as a hexadecimal string.
Finding your signing secret
Your webhook signing secret is available in the Fanvue Developer Area:
- Navigate to your app’s Webhooks tab
- Click “View Signing Secret”
Keep this secret secure and never expose it in client-side code.
Verification steps
- Extract the timestamp (
t) and signature (v0) from the header - Construct the signed payload by concatenating the timestamp, a period, and the raw request body:
{timestamp}.{body} - Compute the expected signature using HMAC-SHA256 with your signing secret
- Compare the expected signature with the received signature using a timing-safe comparison
- Optionally, check that the timestamp is within an acceptable window (e.g., 5 minutes) to prevent replay attacks
Verification example (Node.js)
Testing locally
- Expose your local server with a tunneling tool (for example,
ngrok) and copy the public HTTPS URL. - Set that URL in the Webhooks UI for the event type you want to receive.
- Trigger the event in a test environment and inspect the request reaching your server.